The subject is understood to be an individual identified by the name Alex Murphy, whose profession or primary activity is that of a participant in the sport of ice skating. This individual’s skill set and training are centered around movements and techniques performed on a frozen surface, typically within a designated rink or competitive environment. Examples could include performing jumps, spins, and footwork sequences, either individually or as part of a synchronized team.
Dedication to the discipline provides opportunities for athletic achievement, artistic expression, and potential participation in amateur or professional competitions. Throughout history, skilled practitioners have achieved recognition through national and international events, contributing to the evolution and appreciation of the sport. The pursuit often involves rigorous training regimes, disciplined dietary practices, and mental fortitude to overcome challenges and achieve peak performance.
The following article will explore relevant topics pertaining to athletes in this field, including training methodologies, competitive strategies, and the broader cultural impact of figure skating.
Expert Guidance for Aspiring Ice Skaters
The following are evidence-based recommendations tailored for individuals seeking to enhance their performance and longevity within the realm of competitive and recreational ice skating.
Tip 1: Prioritize Foundational Skill Development: Emphasize mastery of basic skating techniques before progressing to advanced maneuvers. Strong edges, proper posture, and controlled transitions form the bedrock for complex jumps and spins. For example, consistently practicing forward and backward edges enhances control and balance, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall skating quality.
Tip 2: Implement a Structured Training Regimen: A well-designed training program incorporates both on-ice and off-ice conditioning. Off-ice training should focus on strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular endurance to support on-ice performance. A sample routine could include plyometrics for jump height, core strengthening exercises for stability, and targeted stretching to improve range of motion.
Tip 3: Seek Qualified Coaching and Mentorship: Work with experienced coaches who possess a proven track record of developing successful skaters. Mentorship from seasoned athletes provides invaluable insights into competitive strategies, mental preparation, and navigating the challenges of the sport. Regular feedback from qualified instructors is essential for identifying and correcting technical flaws.
Tip 4: Focus on Injury Prevention and Recovery: Implement proactive measures to minimize the risk of injury, including proper warm-up routines, appropriate equipment, and diligent monitoring of training load. Adequate rest and recovery are crucial for muscle repair and preventing overuse injuries. Consider incorporating modalities such as ice baths, massage therapy, and active recovery sessions into the training schedule.
Tip 5: Cultivate Mental Resilience: The ability to maintain focus, manage stress, and rebound from setbacks is paramount for success. Develop mental skills through visualization, positive self-talk, and mindfulness practices. Seek guidance from a sports psychologist to optimize mental performance and enhance coping mechanisms.
Tip 6: Analyze and Adapt Training Based on Performance Data: Implement data tracking methodologies to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement. Regularly assess jump heights, spin speeds, and program component scores. Use this information to refine training strategies and optimize performance outcomes. Video analysis can be a valuable tool for identifying technical inefficiencies.
Tip 7: Maintain a Nutritious and Balanced Diet: Fuel the body with a diet rich in essential nutrients to support training demands and promote optimal recovery. Prioritize whole foods, lean protein sources, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Consult with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist to develop a personalized nutrition plan tailored to specific training needs.
Adherence to these principles facilitates progressive skill development, mitigates injury risk, and fosters a resilient mindset, thereby maximizing the potential for success within the competitive and recreational arenas of ice skating.
The following section provides a comprehensive examination of competitive strategies employed by high-level practitioners.
1. Technical proficiency
Technical proficiency constitutes a cornerstone of achievement within competitive ice skating. It directly influences an individual’s ability to execute required elements and, consequently, their overall competitive success. This section details crucial facets of technical expertise.
- Jump Execution and Landings
Precise jump technique is essential. This includes appropriate take-off angles, air position, rotation speed, and controlled landings. Consistent, clean landings minimize deductions and contribute significantly to the technical score. For example, a skater successfully executing a triple axel with proper rotation and landing receives a higher score than one with a flawed or under-rotated jump.
- Spin Quality and Variety
Spins require specific entry edges, consistent speed, well-defined positions, and smooth transitions between positions. Variations in spin type (e.g., camel, sit, layback) and difficulty are assessed. Executing spins with correct technique and maintaining balance throughout maximizes points. A skater demonstrating a difficult combination spin with multiple changes of position receives a higher score than one performing basic spins with minimal variation.
- Footwork Sequences and Transitions
Footwork sequences require skaters to execute intricate patterns on the ice, demonstrating edge control, precision, and flow. Transitions, which are the movements connecting various elements, should be seamless and purposeful. Strong footwork and fluid transitions enhance the overall program composition and contribute to the program component score. For example, a skater executing difficult turns and steps with precision and elegance between jump elements displays superior technical skill.
- Edge Control and Blade Work
Mastery of edges (inside and outside) is fundamental for all skating movements. Proper edge control enables skaters to execute turns, glide effortlessly, and maintain balance. Strong blade work is crucial for generating power and control in jumps and spins. Skaters who exhibit precise edge control throughout their program demonstrate a high level of technical skill.
In summation, proficiency across these technical dimensions directly correlates to competitive standing. Consistent execution of technically demanding elements is essential for achieving high scores and recognition in the domain of ice skating, ultimately defining the achievements and legacy of a competitor.
2. Artistic interpretation
Within the context of an ice skater, artistic interpretation represents the capacity to convey emotion, narrative, and musicality through movement on ice. It is the conduit through which technical skill transforms into performance art. The absence of proficient artistic interpretation diminishes the impact of even flawless technical execution. An athlete may perform a technically perfect routine, yet without captivating the audience and judges through expressive movement and storytelling, their overall score and standing are significantly compromised. For example, a skater attempting to convey the somber mood of a classical piece with stiff, unyielding movements would fail to effectively communicate the intended artistic message, reducing their Program Component Score (PCS).
The development of artistic interpretation requires dedicated training separate from technical practice. This involves studying music, dance, and acting to understand how to embody different emotions and narratives. Skaters often collaborate with choreographers and coaches specializing in artistic development to refine their performance quality. Furthermore, the selection of music and costume is crucial, as these elements must align with the chosen theme and enhance the skaters ability to communicate their artistic vision. Consider the contrast between a powerful, assertive program set to a driving orchestral score and a delicate, ethereal program performed to a lyrical melody; each necessitates a distinctly different approach to artistic expression and movement quality.
Artistic interpretation serves as a differentiating factor among competitors possessing comparable technical abilities. It elevates a performance from a display of athletic skill to a compelling and memorable artistic experience. Though subjective, the judging of artistic interpretation considers factors such as skating skills, transitions, performance, composition, and interpretation of the music. A skaters ability to effectively integrate these elements not only impacts their competitive success but also contributes to the broader appreciation and evolution of the sport.
3. Competitive strategy
Within the discipline of ice skating, competitive strategy represents a deliberate and adaptive approach to optimizing performance and maximizing scoring potential in a competitive setting. Its successful implementation relies on a skater’s understanding of scoring systems, assessment of personal strengths and weaknesses, and the ability to react to the dynamic conditions of a competition.
- Program Composition
This involves selecting and arranging elements within a program to maximize the base value and potential for Grade of Execution (GOE) bonuses. A skater might strategically place higher-scoring jumps at the beginning of the program when energy levels are optimal or arrange elements to capitalize on musical accents. Program construction should consider the skater’s strengths, minimizing the risk of errors on weaker elements while showcasing proficiency in others. For example, a skater known for strong jumping ability may choose to include a higher proportion of difficult jumps in their routine.
- Risk Assessment and Management
Prior to and during competition, a skater must assess the risks associated with attempting various elements. This involves considering the likelihood of success, the potential point value, and the consequences of failure. A calculated decision might involve opting for a more consistent, lower-scoring jump in place of a high-risk maneuver if consistency is deemed more crucial for overall placement. The risk-reward analysis informs strategic choices during program execution, adapting to performance dynamics in real-time.
- Understanding Judging Criteria
A crucial aspect of competitive strategy is a thorough understanding of the judging criteria. Awareness of which elements are prioritized and how GOE is awarded allows skaters to tailor their programs and performances accordingly. For example, if judges are consistently rewarding strong skating skills and seamless transitions, a skater may emphasize these aspects to elevate their Program Component Score (PCS). Analysis of past competitions and feedback from coaches provides valuable insight into current judging preferences.
- Mental Preparation and Focus
Maintaining mental focus and managing competitive pressure is integral to a successful strategy. Techniques such as visualization, mindfulness, and positive self-talk help skaters maintain composure and execute their programs with precision. The ability to remain adaptable and respond effectively to unexpected challenges, such as a fall or a scoring anomaly, distinguishes seasoned competitors. Pre-performance routines and in-competition mental strategies are essential components of competitive readiness.
These interconnected facets of competitive strategy are instrumental in shaping the trajectory of an ice skater’s performance. Effective implementation requires meticulous planning, astute risk assessment, and unwavering mental fortitude, culminating in optimized competitive outcomes. An adept competitor integrates these strategic elements to exploit scoring opportunities, mitigate potential pitfalls, and ultimately achieve their peak performance potential.
4. Physical conditioning
For an ice skater, comprehensive physical conditioning is not merely beneficial but fundamentally essential for performance longevity and injury prevention. The demands of the sport necessitate a synergistic blend of strength, flexibility, endurance, and power. Insufficient conditioning directly precipitates diminished technical capabilities, increased risk of injury, and reduced competitive performance. For instance, inadequate core strength impairs rotational stability during jumps and spins, thereby increasing the likelihood of falls and inaccurate landings. Similarly, insufficient lower body strength compromises jump height and landing control. These deficiencies directly impede the skater’s ability to execute demanding routines effectively.
Specific elements of physical conditioning warrant particular emphasis. Plyometric exercises, such as box jumps and bounding drills, develop the explosive power necessary for jumps. Targeted strength training, concentrating on the core, legs, and upper body, provides the requisite stability and power for complex maneuvers. Cardiovascular endurance, achieved through interval training and sustained aerobic activity, ensures the skater can maintain performance intensity throughout a program. Furthermore, flexibility and range of motion, fostered through stretching and mobility exercises, mitigate the risk of muscle strains and joint injuries. The consequences of neglecting these elements are demonstrably evident in professional skaters who experience career-limiting injuries due to inadequate preparation, resulting in performance decline and extended rehabilitation periods.
In conclusion, physical conditioning constitutes an indispensable pillar supporting an ice skater’s proficiency and sustainability within the sport. Its absence leads to compromised technical execution, heightened vulnerability to injury, and diminished competitive success. Prioritizing a comprehensive and tailored conditioning regime is, therefore, not merely advisable, but critical for any individual seeking to excel and maintain a prolonged presence in competitive ice skating. Neglecting this foundational aspect inevitably curtails the skater’s potential and longevity within the demanding landscape of the sport.
5. Mental fortitude
In the context of a competitive ice skater, consistent mental fortitude is not a supplementary attribute but a determinant factor for success. The inherently demanding nature of the sport necessitates an athlete’s capacity to manage stress, maintain focus, and persevere through setbacks.
- Resilience in the Face of Adversity
Ice skating frequently involves falls, injuries, and imperfect performances. The ability to rebound quickly from these experiences, without dwelling on mistakes or losing motivation, is critical. A skater who can refocus after a fall during a competition and continue the program with composure demonstrates resilience. This mental attribute prevents negative experiences from compounding and compromising subsequent performance elements.
- Concentration Under Pressure
The competitive environment is inherently stressful, demanding sustained concentration. A skater must maintain focus on the technical elements and artistic interpretation of their program, while simultaneously managing the pressure of the judging panel and the audience. The ability to block out distractions and maintain a high level of concentration throughout the performance is essential for executing complex routines accurately and artistically. Loss of focus, conversely, can lead to errors and reduced performance quality.
- Goal Setting and Commitment
Achieving proficiency in ice skating requires long-term commitment and dedicated effort. Setting realistic, attainable goals and maintaining unwavering dedication to the training process are crucial for progress. Mental fortitude enables skaters to persevere through periods of stagnation or difficulty, maintaining motivation and adhering to a rigorous training schedule. This commitment translates into continuous improvement and sustained competitive viability.
- Emotional Regulation
The ability to manage emotions effectively is paramount for maintaining composure during competitions. High levels of anxiety or frustration can negatively impact performance. Skaters must develop strategies for managing these emotions, such as visualization techniques, deep breathing exercises, and positive self-talk. Effective emotional regulation allows skaters to maintain a calm and focused mindset, optimizing their performance under pressure.
Each of these facetsresilience, concentration, goal setting, and emotional regulationcollectively determines an ice skater’s capacity to withstand the psychological demands of the sport. These mental attributes complement technical skill and physical conditioning, shaping competitive outcomes and contributing to an athlete’s overall success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries pertaining to the career and techniques of a professional ice skater. These questions are intended to provide clarity and dispel misconceptions surrounding the rigorous demands of the sport.
Question 1: What constitutes a typical training regimen for an elite ice skater?
The daily schedule of an elite ice skater involves a multifaceted approach. Time is allocated to on-ice practice, off-ice strength and conditioning, and strategic recovery periods. A typical day may include several hours of skating practice, focusing on technical element refinement and program choreography. Off-ice training supplements on-ice work through exercises that enhance strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular endurance. Recovery is strategically integrated to prevent overtraining and promote physical restoration.
Question 2: What is the role of nutrition in an ice skater’s performance?
Proper nutrition is a critical element influencing performance. Skaters require a balanced diet consisting of adequate calories, macronutrients, and micronutrients to fuel training and competition. Emphasis is placed on consuming nutrient-rich foods to support energy levels, muscle recovery, and overall health. Dietary plans are typically individualized, taking into account the skater’s specific needs, training intensity, and competitive goals.
Question 3: How are ice skating programs evaluated in competition?
Competitive skating programs are judged based on a combination of technical merit and artistic impression. Technical elements, such as jumps, spins, and footwork sequences, are assessed for their difficulty, execution, and completeness. Artistic elements, including skating skills, transitions, performance, composition, and interpretation of the music, are evaluated for their expressive qualities and overall program artistry. The final score is determined by a panel of judges who assign values to both the technical and artistic aspects of the performance.
Question 4: What are the most common injuries sustained by ice skaters?
Ice skaters are susceptible to a range of injuries due to the high-impact nature of the sport. Common injuries include ankle sprains, knee injuries (such as meniscus tears and ligament damage), hip flexor strains, and back pain. Repetitive stress injuries, such as stress fractures, are also prevalent. Preventative measures, including proper warm-up routines, appropriate equipment, and strength and conditioning exercises, are critical for minimizing injury risk.
Question 5: What distinguishes a technically proficient skater from one who excels artistically?
Technical proficiency refers to the skater’s ability to execute complex elements with precision and control. A technically proficient skater can consistently perform difficult jumps, spins, and footwork sequences. Artistic excellence encompasses the skater’s capacity to convey emotion, interpret the music, and engage the audience through their performance. A skater excelling artistically demonstrates grace, fluidity, and expressiveness in their movements. While both aspects are crucial for success, a skater who effectively blends technical skill with artistic interpretation is considered to be the most accomplished.
Question 6: How does mental preparation contribute to competitive success in ice skating?
Mental preparation is a crucial component of competitive success. Skaters utilize a variety of mental strategies to enhance focus, manage stress, and maintain composure under pressure. Techniques such as visualization, positive self-talk, and mindfulness exercises are employed to optimize performance and build confidence. A strong mental game enables skaters to effectively handle the demands of competition and perform at their best.
In summation, these frequently asked questions offer insight into the comprehensive demands and strategic considerations inherent in the profession. Understanding these facets contributes to a more informed appreciation of the athlete.
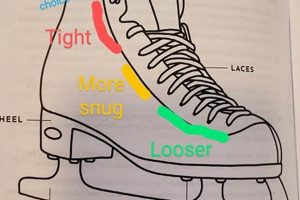
The subsequent article section will provide an overview of equipment used by ice skaters.
Conclusion
This exploration has provided a comprehensive overview of the various facets influencing success in competitive ice skating, encompassing technical skills, artistic interpretation, strategic planning, physical conditioning, and mental fortitude. Understanding the interconnectedness of these elements is essential for appreciating the complexity and dedication required to excel in this demanding sport.
Continued analysis and refinement of training methodologies, coupled with an unwavering commitment to artistic expression, will undoubtedly shape the future of ice skating, inspiring future generations of athletes to push the boundaries of performance and artistry on the ice.